On October 28 2025, NVIDIA and Nokia announced a partnership that will accelerate the transition from 5G-Advanced to AI-native 6G.
The collaboration introduces NVIDIA’s Aerial RAN Computer (ARC Pro) — a 6G-ready platform built to unify computing, connectivity, and sensing — while Nokia integrates AI-RAN software directly onto this architecture. Field trials with T-Mobile US begin in 2026, and analysts project the AI-RAN market to exceed $200 billion by 2030.

As these intelligent networks push processing power to the edge, each tower effectively becomes a micro-data-center — dense with radios, GPUs, and sensors.
But as every engineer knows, innovation at the edge also brings environmental stress. AI-RAN architectures concentrate processing power in compact outdoor enclosures that operate through extreme temperature swings. Inside those sealed boxes live the heart of every modern wireless connection — MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) systems.
MIMO: The Engine of 5G and 6G Connectivity
MIMO, short for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output, is a wireless communication technology that uses multiple antennas at both the transmitting source (like a 5G tower) and the receiving device (such as a smartphone or vehicle module).
By sending and receiving multiple data streams simultaneously, MIMO dramatically boosts signal capacity, reliability, and data speed — making it the backbone of today’s high-performance networks.
In AI-RAN and 6G architectures, MIMO modules are becoming even more advanced. Each antenna array is paired with computing chips, sensors, and active components that run continuously.
These compact, sealed enclosures face frequent heating and cooling cycles — and with them, a high risk of condensation.
When warm, humid air meets the cooler surfaces of an outdoor base station, it crosses the dew point. Moisture then condenses into microscopic droplets on circuit boards and connectors, causing corrosion, short circuits, and gradual signal degradation. For MIMO systems, even minor condensation can distort phase alignment or antenna gain — undermining the very precision that makes MIMO powerful.

Traditional fixes such as vent membranes, heaters, or silica-gel bags only delay the problem:
-
Heaters consume power and accelerate component aging.
-
Vents introduce dust and pollution.
-
Silica gel, CaCl₂, and MgCl₂ desiccants saturate rapidly and leak corrosive liquid.
The industry needed a passive, maintenance-free, and sustainable way to keep enclosures above the dew point — and that’s where ATMOSIScience’s Fiber Technology redefines environmental control.
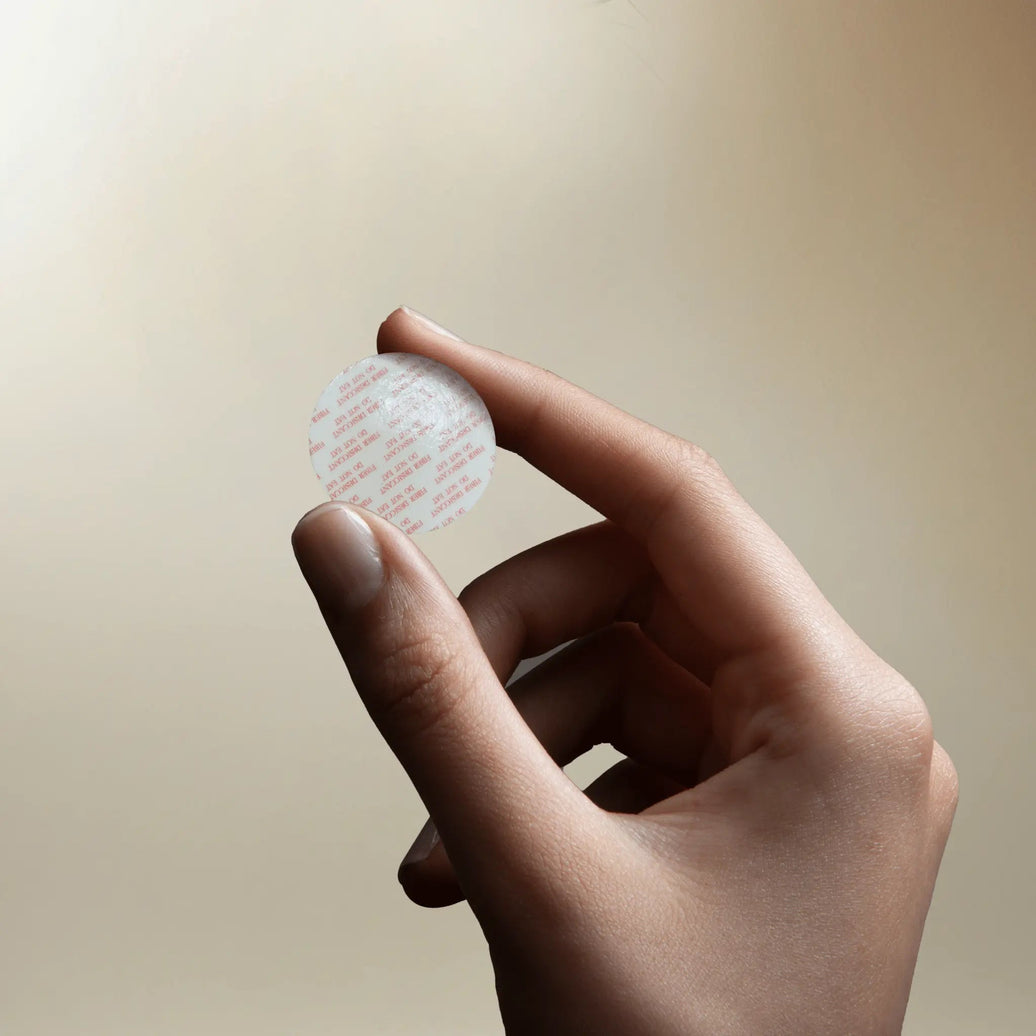
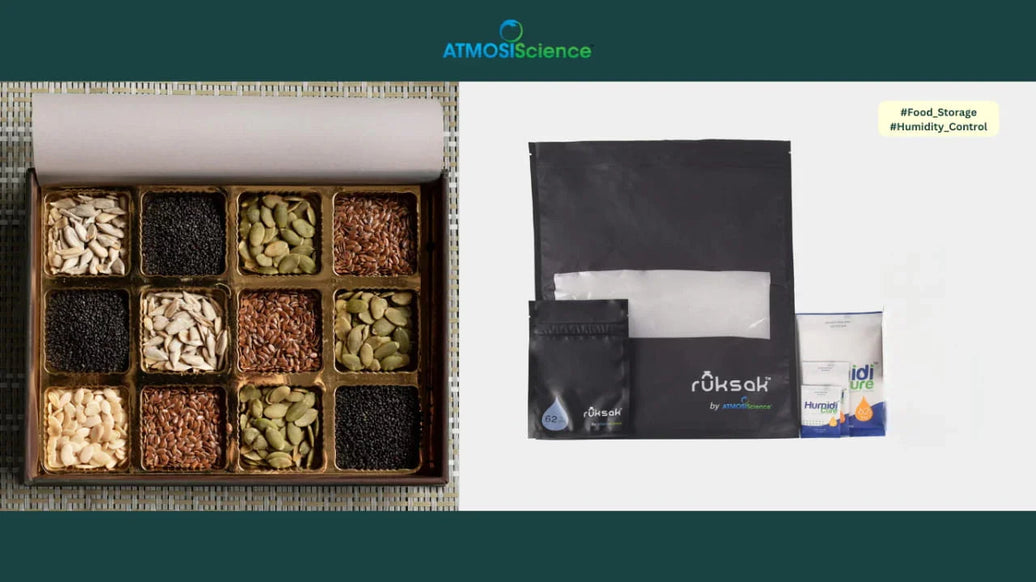
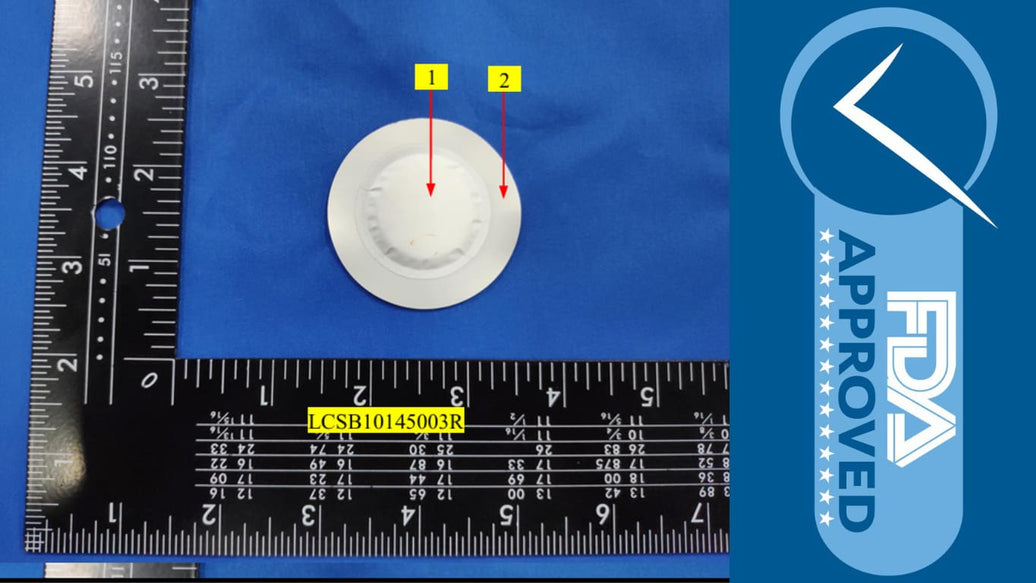
The ATMOSIScience Anti-condensation Fiber Pack
ATMOSIScience’s Anti-condensation Fiber Pack is a material-science solution engineered specifically for humidity control in sensitive electronic micro-environments — including MIMO modules, RRUs, AAUs, and energy-storage systems.
Unlike conventional desiccants that absorb moisture once and then fail, the Fiber Pack uses a built-in two-way humidity-control fiber that dynamically absorbs and releases moisture to maintain stable relative humidity inside sealed enclosures.
This reversible mechanism prevents dew formation before it begins — keeping MIMO systems within their optimal humidity range.
Key technical highlights drawn from lab validation
-
>100 % water absorption in 24 h @ 40 °C / 95 % RH with no surface leakage
-
>40 % absorption + release capacity @ 40 °C / 50–70 % RH
-
10 + years usable life, < 20 % performance degradation after thermal-humidity cycling
-
Halogen-free, non-corrosive, biodegradable, and safe for metals and optics
-
Compact (≈ 60 × 30 × 4 mm) with adhesive backing for quick installation on cabinet walls or lids

Each pack consists of a breathable outer shell and an inner core of ATMOSIScience’s proprietary fiber. An adhesive layer allows engineers to place it precisely where condensation typically starts — on the inner wall, door, or near the antenna electronics of MIMO units.
Because it contains no liquids or salts, it poses zero corrosion risk to high-frequency circuitry and connectors.
Material Science That Matters
ATMOSIScience technology already protects sensitive environments in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and museum-grade preservation.
In telecom, it has been validated for 5G and 6G tower applications, including MIMO, RRU, and AAU systems, where day–night temperature differences can exceed 30 °C.

The pack’s 10-year reusability and zero-leak construction make it ideal for maintenance-free operation in remote base stations — aligning with operators’ sustainability and reliability goals.
Paired with HaaS (Humidity as a Service), ATMOSIScience’s cloud-connected sensor system, network teams can monitor relative humidity and dew-point data in real time, schedule proactive maintenance, and document environmental stability across entire MIMO fleets.

As NVIDIA × Nokia’s AI-RAN defines the next generation of intelligent connectivity, ATMOSIScience ensures the environment it relies on stays scientifically controlled — consistent, verifiable, and sustainable.

If you’re designing 5G or 6G infrastructure and want to build environmental stability into your system architecture, book a technical consultation with our team.